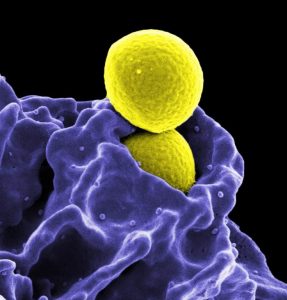
 Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a drug resistant strain of a common bacteria found on the skin and in the nose of healthy people. Skin infections of MRSA are the most common, causing redness, warmth, pus and a wound that does not heal. It is sometimes mistaken for a spider or insect bite. MRSA is most often spread by direct person-to-person contact and can also be spread by contact with contaminated items or surfaces. MRSA normally does not cause disease unless it enters an opening in the skin.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a drug resistant strain of a common bacteria found on the skin and in the nose of healthy people. Skin infections of MRSA are the most common, causing redness, warmth, pus and a wound that does not heal. It is sometimes mistaken for a spider or insect bite. MRSA is most often spread by direct person-to-person contact and can also be spread by contact with contaminated items or surfaces. MRSA normally does not cause disease unless it enters an opening in the skin.
If you suspect you have an MRSA skin infection, cover the area with a bandage and contact your healthcare provider. Until the infection is healed, make sure to wash your hands frequently, keep the area covered with clean bandages, and do not share personal items. See the additional resources below or contact your local health department if you have more questions about MRSA.
Additional Resources
