Definitions
Genome Sequencing: A variety of laboratory procedures that provide detailed information about the genetic makeup of infectious disease pathogens (germs) that are making people sick.
Gene: A specific sequence of DNA or RNA found at a specific location in a genome. Each gene encodes a function within the human body or other organisms (for example, there are specific genes that produce eye color).
Genome: All of the DNA or RNA found in a cell or virus.
Mutation: A change in the genetic sequence of DNA or RNA where nucleotides have been altered, inserted, or deleted.
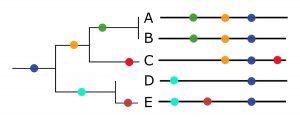
Phylogenetic Tree: A tree-like diagram that shows mutational differences between sequenced DNA or RNA. These diagrams show evolutionary changes and genetic relationships between organisms over time.